

(g) “Lesson Fee” is the combined hourly fee of the Tutor fee and the Website Fee. (f) “Independent Tutor” means a person that has appropriate qualifications and experience to provide tuition services in the areas advertised by the Tutor on the Shalom Education Website, with the intention of entering into a Contract. (e) “Failed Payment” means an outstanding Lesson Fee, for which Shalom Education has been unable to make a successful charge against the payment details provided by the Tutee (d) “Complaint” means a claim by a Tutee that the service provided by a Tutor falls below the standards the tutee expected of a Booking Tutor. (c) “Booking Tutor” means a Tutor who uses the Shalom Education Website to schedule tuition lessons and uses Shalom Education as an agent to collects payments on his behalf. (b) Contract” means the agreement between the Tutor and the Tutee for the Tutor to perform tuition services for the Tutee or the Tutee’s nominee. (a) “Booking” means tuition lessons that are scheduled using the Shalom Education Website. The following expressions are given the following meanings:
Reactivity series update#
You can update your email address within your Personal Info section once you sign in.
Please make sure that the email address we have stored for you is current and you can access it. These Terms and Conditions may change from time to time.
Reactivity series registration#
Continued registration with Shalom Educationist deemed acceptance of these Terms and Conditions. Please take a time to read and understand the Terms and Conditions before registering for the Shalom Education Website.

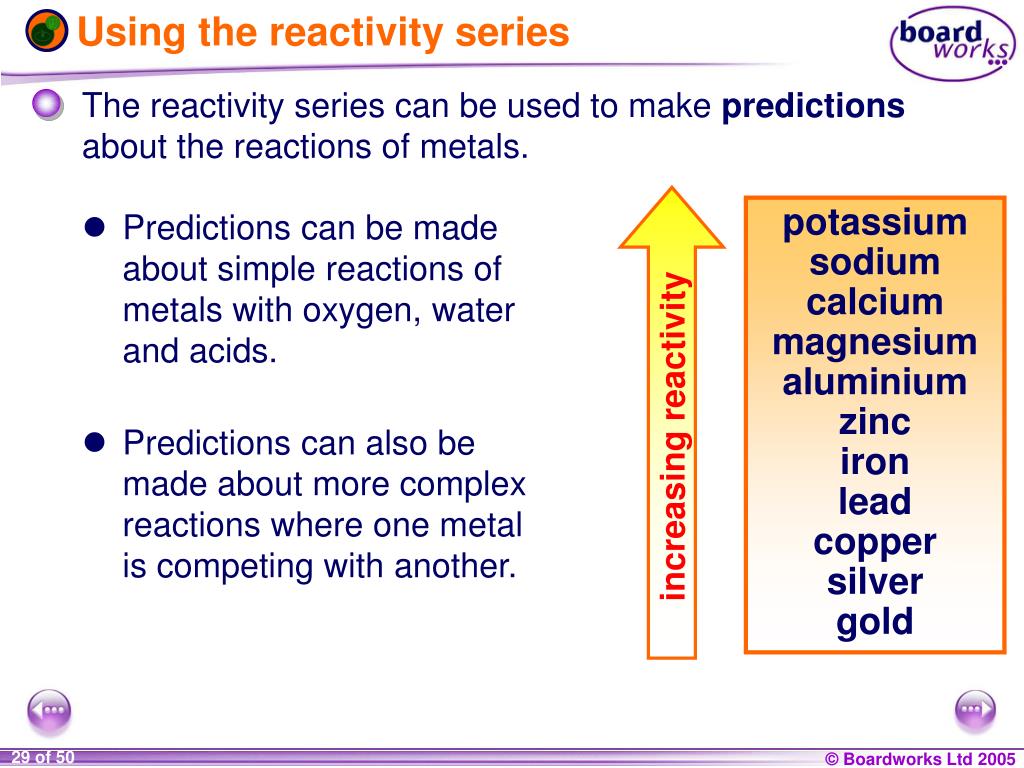
It does not store any personal data.Ĭontained here are the Terms and Conditions which you must read and agree to before registering for the Shalom Education Website. The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. Potassium + Hydrochloric acid → Potassium chloride + HydrogenĢ K (s) + 2HCl (aq) → 2KCl (aq) + H 2 (g) Most metals react with dilute acids, such as HCl, to form a salt and hydrogen.įor example, potassium reacts rapidly with dilute hydrochloric acid to form potassium chloride and hydrogen gas. Lithium + Water → Lithium hydroxide + HydrogenĢLi (s) + 2H 2O (l) → 2LiOH (aq) + H 2 (g) Reactions of Metals with Acids Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide + Hydrogenįor example, lithium reacts with cold water to form lithium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Some metals react with cold water to form a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Reactivity series series#
Whereas, metals at the bottom of the series do not lose electrons easily, some are even resistant to oxidation. The metals at the top of the series oxidise (lose electrons) more easily. As it is a measure of how reactive a metal is. The more easily a metal atom loses electrons, the higher the metals is placed in the reactivity series. Metals lose electrons to form positive ions (cations).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
